How Graphics Cards Work: A Simple Explanation
Graphics cards, also known as GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), are essential components in modern computers, responsible for rendering images, videos, and animations. Whether you’re gaming, editing videos, or just browsing the web, your GPU plays a crucial role in delivering smooth visuals. But how exactly do these powerful pieces of hardware work? Let’s break it down in a simple, calm manner.

The Basics: What Is a Graphics Card?
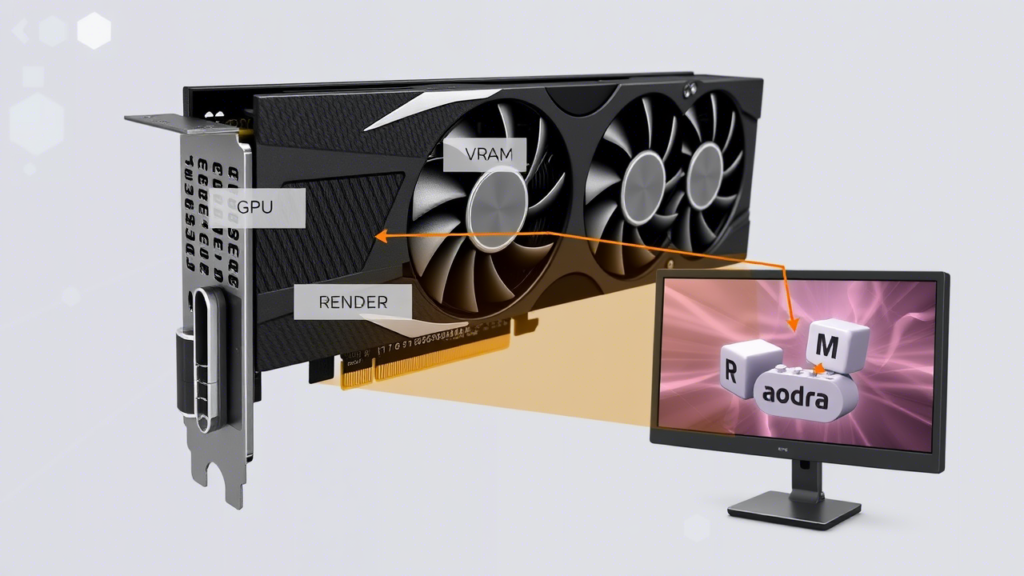
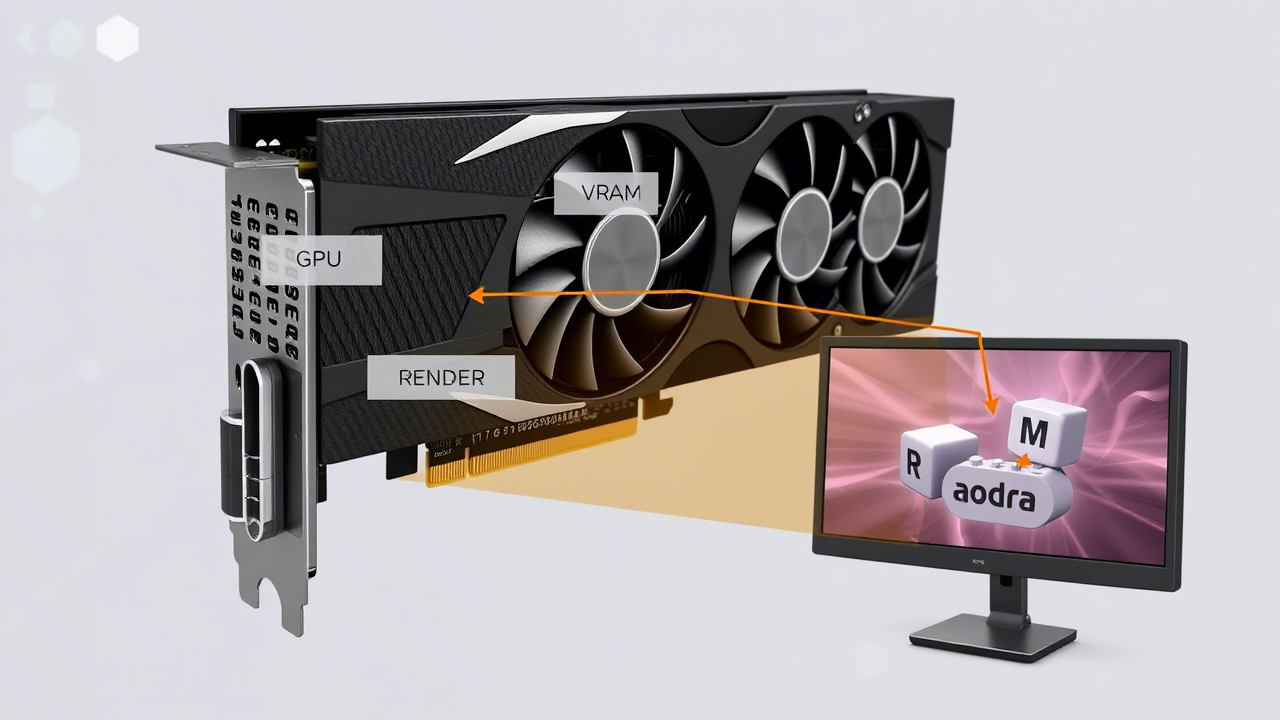
A graphics card is a dedicated processor designed to handle complex visual computations. Unlike the CPU (Central Processing Unit), which manages general tasks, the GPU specializes in parallel processing—performing many calculations simultaneously. This makes it exceptionally efficient for rendering graphics.
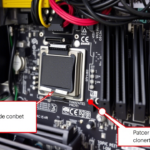
A typical graphics card consists of:
- GPU Chip: The core processor that performs calculations.
- VRAM (Video RAM): High-speed memory that stores textures, frames, and other graphical data.
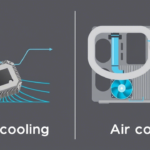
- Cooling System: Fans or liquid cooling to prevent overheating.
- Output Ports: HDMI, DisplayPort, or others to connect to monitors.
- Power Connectors: Since GPUs consume significant power, they often need direct power from the PSU (Power Supply Unit).
The Rendering Process
When you see an image on your screen, the GPU has gone through several steps to create it:
- Data Reception – The CPU sends instructions about what needs to be displayed (e.g., a 3D game scene).
- Vertex Processing – The GPU calculates the positions of 3D objects (vertices) in a scene.
- Rasterization – The 3D models are converted into 2D pixels (rasterization).
- Shading & Texturing – Colors, lighting, and textures are applied to make the image realistic.
- Output to Display – The final image is sent to your monitor.
This entire process happens in milliseconds, allowing for smooth animations and high frame rates.
Why Are GPUs So Powerful for Graphics?
CPUs are great at handling sequential tasks, but GPUs excel at parallel processing. A modern GPU has thousands of smaller cores designed to work simultaneously, making them ideal for:
- Real-time rendering (games, VR)
- Video editing & 3D modeling
- Machine learning & AI tasks
Integrated vs. Dedicated Graphics
Some computers use integrated graphics, where the GPU is built into the CPU. These are power-efficient but less powerful, suitable for everyday tasks. Dedicated graphics cards, like those from NVIDIA or AMD, are separate components with their own memory, offering much higher performance for gaming and professional work.
Conclusion
Graphics cards are fascinating pieces of technology that transform raw data into the vibrant visuals we see on our screens. By handling thousands of calculations at once, they enable everything from high-end gaming to smooth video playback. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, understanding how GPUs work can help you appreciate the complexity behind every pixel.
If you found this explanation helpful, feel free to explore more about GPU architectures, ray tracing, or how AI is changing graphics technology. The world of GPUs is vast and ever-evolving!